In the bustling cities of modern India, the issue of urban waste management has reached critical levels. Rapid urbanization, population growth, and changing consumption patterns have led to an exponential increase in the generation of municipal solid waste (MSW), posing significant environmental, health, and socioeconomic challenges. However, amidst these challenges lie opportunities for innovative solutions, with waste processing machines such as balers, shredders, and compactors emerging as crucial tools in the battle against urban waste hazards. Let’s delve into the pressing issues surrounding urban waste in India and explore how waste processing machines can play a pivotal role in addressing them.
Urban Waste Hazards in India
India’s urban areas are grappling with a myriad of waste-related hazards, including:
1. Environmental Pollution:
Improper disposal of waste, including plastics, electronic waste, and organic matter, pollutes air, water bodies, and soil, leading to environmental degradation and ecosystem harm.
2. Health Risks:
Accumulation of unmanaged waste creates breeding grounds for disease vectors such as mosquitoes and rodents, increasing the risk of vector-borne diseases and posing health hazards to residents, particularly in densely populated urban settlements.
3. Resource Depletion:
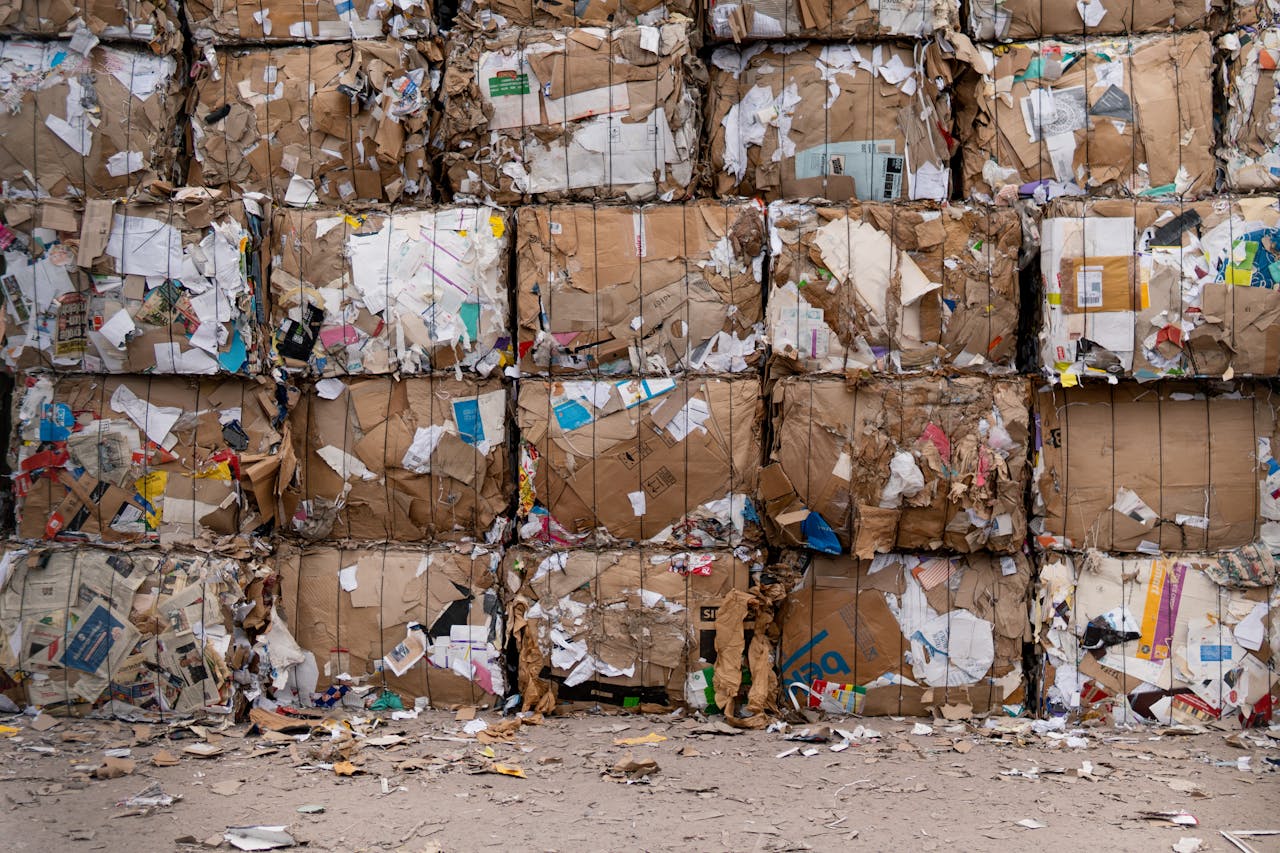
Inefficient waste management practices result in the loss of valuable resources, including recyclable materials such as paper, plastics, and metals, which could otherwise be recovered, recycled, and reused.
4. Aesthetic Degradation:
Piles of uncollected waste mar the urban landscape, diminishing the aesthetic appeal of cities and undermining tourism potential and local economic development efforts.
The Role of Waste Processing Machines
Waste processing machines, including balers, shredders, compactors, and sorting systems, offer a comprehensive approach to managing urban waste in India. Here’s how these machines can make a difference:
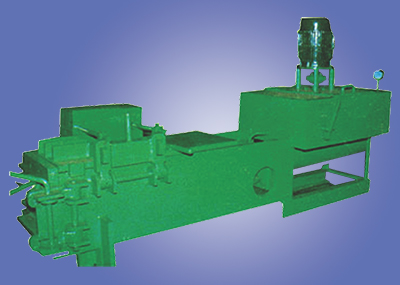
1. Balers:
Balers compress and bind recyclable materials such as cardboard, paper, plastics, and aluminum cans into compact bales, making them easier to store, transport, and recycle. By compacting recyclables at source or in recycling facilities, balers facilitate efficient handling and processing of materials, maximizing resource recovery and reducing landfill dependence.
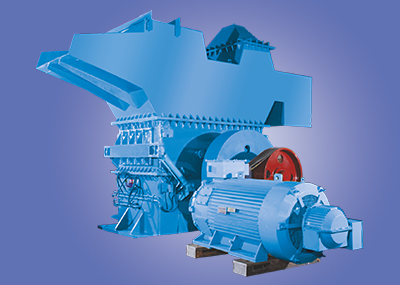
2. Shredders:
Shredders break down bulky waste items, including furniture, appliances, electronic waste, and organic matter, into smaller, more manageable pieces. This preprocessing step enhances the efficiency of downstream waste processing operations, such as composting, recycling, and energy recovery, while also reducing transportation costs and landfill space requirements.
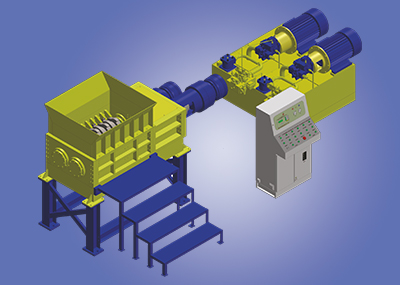
3. Compactors:
Compactors compress non-recyclable waste streams, such as mixed MSW and residual waste, into dense, space-saving blocks or bags. By reducing the volume of waste, compactors minimize the frequency of waste collection trips, optimize transportation logistics, and alleviate the strain on landfill capacities, thereby promoting sustainable waste management practices.
4. Sorting Systems:
Automated sorting systems utilize sensors, conveyor belts, and robotic arms to segregate mixed waste streams into distinct fractions based on material composition, size, and type. By automating the sorting process, these systems enhance the efficiency and accuracy of recycling operations, ensuring higher purity levels in recovered materials and minimizing contamination risks.
Conclusion: Towards Sustainable Urban Waste Management
In the quest for sustainable urban development, effective waste management is non-negotiable. Waste processing machines offer a path forward, enabling cities in India to tackle urban waste hazards head-on while unlocking opportunities for resource recovery, environmental stewardship, and public health improvement. However, realizing the full potential of these machines requires a concerted effort from policymakers, waste management authorities, private sector stakeholders, and citizens alike. By embracing innovation, collaboration, and proactive measures, India can pave the way towards a cleaner, greener, and more resilient urban future for generations to come.